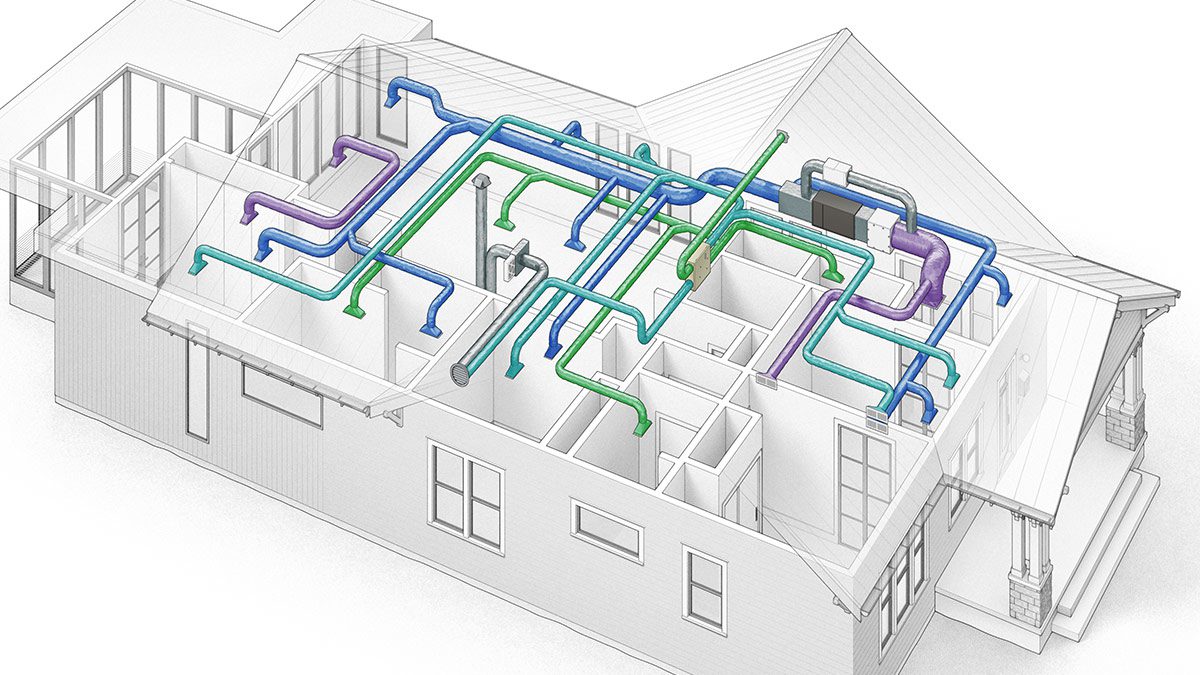
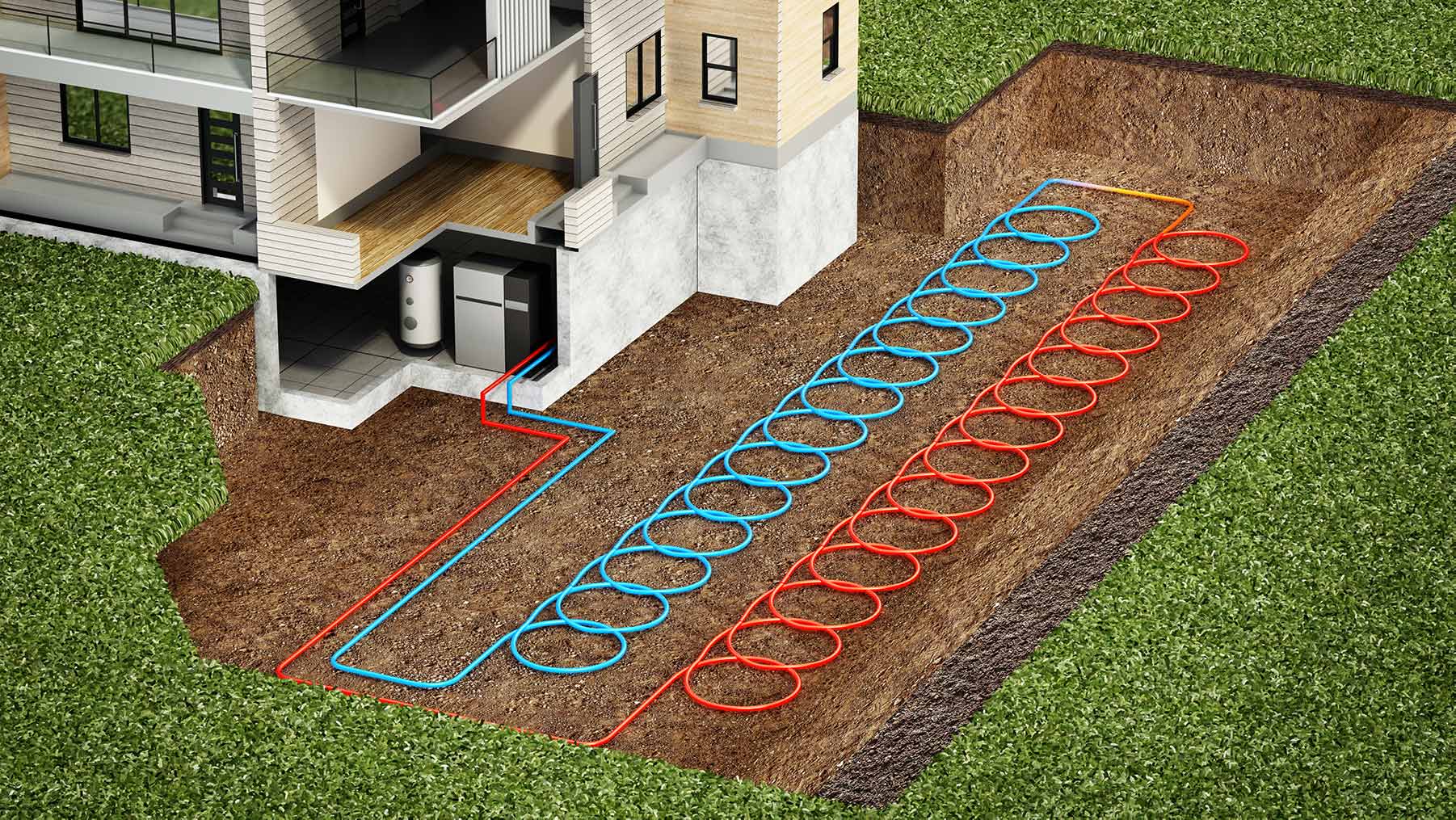
Climate change is no longer a distant environmental concern—it is a present-day engineering challenge. Rising global temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and stricter energy regulations are reshaping how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are designed, installed, and operated. Modern HVAC design must now balance comfort, resilience, efficiency, and sustainability in ways that were not required just a decade ago.
The Growing Climate Pressure on Buildings
Buildings account for a significant share of global energy consumption, and HVAC systems represent the largest portion of that demand. As heatwaves intensify and winters become more erratic, HVAC systems are being pushed harder and longer than ever before.
Key climate-driven pressures include:
-
Longer cooling seasons and shorter shoulder seasons
-
Increased peak-load demand during extreme heat
-
Greater risk of system failure due to weather stress
-
Rising energy costs and carbon reduction mandates
These pressures are forcing a fundamental rethink of HVAC design strategies.
Shift Toward Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems
One of the most visible impacts of climate change on HVAC design is the accelerated push for energy efficiency. Designers are prioritizing systems that deliver comfort while consuming less power.
Design strategies gaining traction
-
High-efficiency heat pumps replacing fossil-fuel-based systems
-
Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems for precise zoning control
-
Enhanced insulation and airtight building envelopes
-
Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) to reduce heating and cooling loads
Efficiency is no longer a value-add—it is a baseline expectation.
HVAC Systems Built for Extreme Weather Resilience
Climate change has increased the frequency of heatwaves, cold snaps, floods, and storms. HVAC systems must now be engineered to perform reliably under extreme and volatile conditions.
Resilient design considerations
-
Components rated for higher temperature thresholds
-
Elevated outdoor units in flood-prone areas
-
Corrosion-resistant materials for humid and coastal regions
-
Redundant system configurations for mission-critical buildings
Resilience-focused HVAC design minimizes downtime and protects occupant safety during climate emergencies.
Electrification and the Decline of Fossil Fuels
Decarbonization goals are driving a rapid shift away from gas- and oil-based HVAC systems. Electrification is becoming central to climate-responsive HVAC design.
Why electrification matters
-
Reduces direct on-site carbon emissions
-
Enables integration with renewable energy sources
-
Aligns with net-zero and carbon-neutral building targets
-
Improves long-term regulatory compliance
All-electric HVAC systems, particularly heat pumps, are now considered a cornerstone of sustainable building design.
Smart HVAC Design and Climate Adaptation
Advanced controls and automation are playing a critical role in adapting HVAC systems to changing climate conditions. Smart HVAC systems use data to continuously optimize performance.
Smart features shaping modern HVAC design
-
Real-time temperature and occupancy sensors
-
AI-driven load forecasting
-
Demand-response compatibility with utility grids
-
Predictive maintenance to prevent climate-related failures
These systems improve comfort while reducing energy waste and operational costs.
Indoor Air Quality in a Warming World
Climate change also affects indoor air quality (IAQ). Increased wildfire smoke, humidity, allergens, and urban pollution are forcing HVAC designers to focus more on air filtration and ventilation.
IAQ-focused design enhancements
-
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) and MERV-rated filters
-
Humidity control to prevent mold growth
-
Increased fresh air ventilation with energy recovery
-
Monitoring systems for CO₂ and particulate levels
Healthy indoor environments are now inseparable from climate-aware HVAC design.
Regulatory Influence on HVAC Design
Governments and municipalities worldwide are introducing stricter building codes to address climate change. These regulations directly influence HVAC system selection and design.
Common regulatory drivers include:
-
Energy performance standards
-
Emissions caps for buildings
-
Mandatory energy benchmarking
-
Incentives for high-efficiency and renewable systems
HVAC designers must stay ahead of evolving codes to ensure compliance and future-proof installations.
The Future of Climate-Responsive HVAC Design
As climate impacts intensify, HVAC design will continue evolving toward systems that are adaptive, low-carbon, and intelligent. Future-ready HVAC solutions will integrate seamlessly with building architecture, renewable energy, and smart infrastructure.
The result is a built environment that remains comfortable and efficient—even as the climate becomes more unpredictable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does climate change directly affect HVAC system sizing?
Rising temperatures increase cooling loads, requiring systems to be sized for higher peak demand without sacrificing efficiency during moderate conditions.
Are heat pumps effective in extreme climates?
Yes. Modern heat pumps are designed to operate efficiently in both very hot and very cold climates when properly selected and installed.
Does climate change increase HVAC maintenance needs?
Extreme weather can accelerate wear on components, making proactive maintenance and monitoring more important than ever.
How do smart HVAC systems help reduce carbon emissions?
They optimize energy use in real time, reduce waste, and support demand-response programs that lower overall grid emissions.
Is indoor air quality becoming more important due to climate change?
Absolutely. Wildfires, humidity, and pollution make advanced filtration and ventilation essential parts of HVAC design.
What role do building codes play in climate-driven HVAC design?
Building codes set efficiency and emissions standards that directly shape HVAC technology choices and system configurations.
Can HVAC systems help buildings reach net-zero goals?
Yes. High-efficiency, all-electric HVAC systems paired with renewable energy are critical to achieving net-zero and low-carbon buildings.